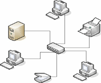
Computer Network
A computer network is a collection of computers and devices connected by communications channels that facilitates communications among users and allows users to share resources with other users.
Types of Network

LAN
A local area network (LAN) is a network that connects computers and devices in a limited geographical area such as home, school, computer laboratory, office building, or closely positioned group of buildings. Each computer or device on the network is a node.

MAN
MAN stands for Metropolitan Area Network. It refers to a network of computers within a city. It is usually the interconnection between various LAN’s in a particular geographical area like a metropolitan city such as Delhi.
WAN
Wide area networking combines multiple LANs that are geographically separate. This is accomplished by connecting the different LANs using services such as dedicated leased phone lines, dial-up phone lines (both synchronous and asynchronous), satellite links, and data packet carrier services.
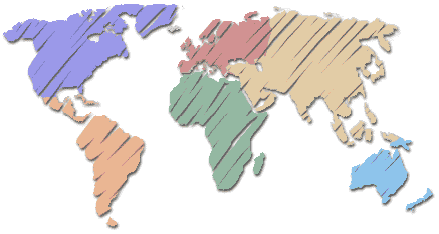
INTERNET
The Internet is a system of linked networks that are worldwide in scope and facilitate data communication services such as remote login, file transfer, electronic mail, the World Wide Web and newsgroups.
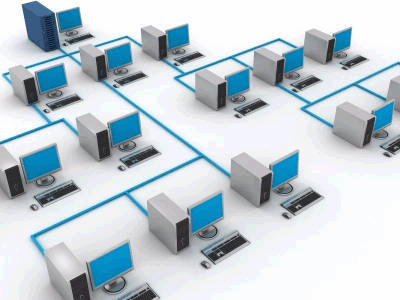
INTRANET
With the advancements made in browser-based software for the Internet, many private organizations are implementing intranets. An intranet is a private network utilizing Internet-type tools, but available only within that organization. For large organizations, an intranet provides an easy access mode to corporate information for employees.
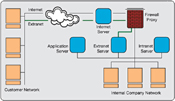
EXTRANET
An extranet is a network that is limited in scope to a single organization or entity and also has limited connections to the networks of one or more other usually, but not necessarily, trusted organizations or entities (e.g., a company's customers may be given access to some part of its intranet creating in this way an extranet, while at the same time the customers may not be considered 'trusted' from a security standpoint).